Process for Regulation of Lactic Acid Fermentation in Wine Production by Magnetic Elimination of Bacteria
| Publication Number: |
SI24998A |
| Application Date: |
6. 5. 2015 |
| Assignee/Applicant: |
Jožef Stefan Institute [SI], University of Ljubljani [SI] |
| Inventor: |
Peter Dušak, Marin Berovič, Darko Makovec |
| Title: |
Postopek za uravnavanje mlečnokislinske fermentacije pri proizvodnji vina z magnetnim izločanjem bakterij [SL], Process for Regulation of Lactic Acid Fermentation in Wine Production by Magnetic Elimination of Bacteria [EN] |
| Description: |
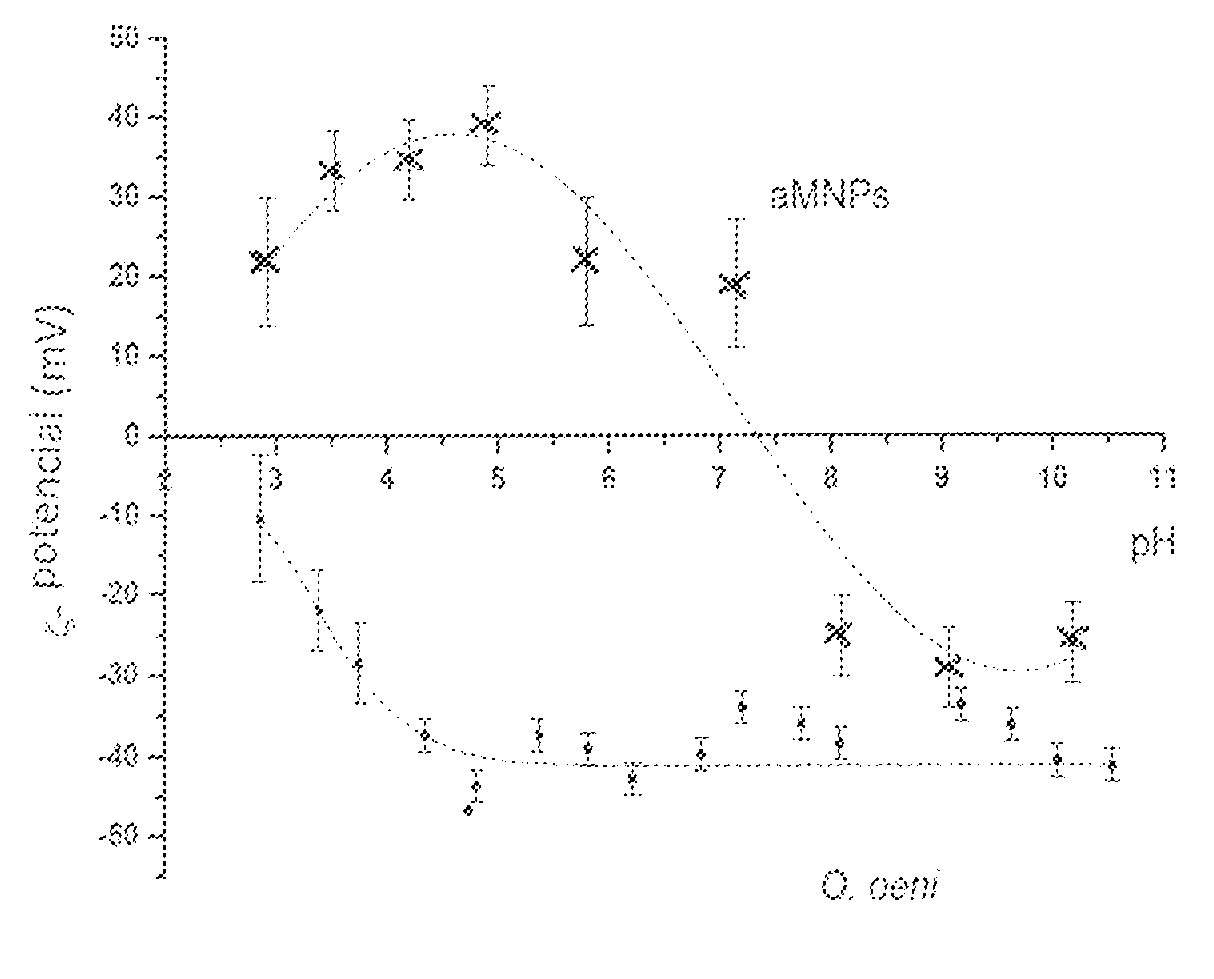
The subject of the invention is a process that allows the control of lactic acid fermentation of wine and is based on the use of magnetic particles. The production of wine is based on fermentation of must, which covers two fermentation processes; alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation. Lactic acid or secondary fermentation, which usually begins after alcoholic fermentation, is a desirable process, as it reduces the acidity of the wine, strengthens the organoleptic characteristics of the wine and improves the microbiological stability of the wine. For known processes, acid-acid fermentations with addition of lactic acid bacteria, such as Oenococcus oeni, to must. Lactic bacteria convert malic acid into lactic acid and carbon dioxide. A technical problem that is not satisfactorily solved is the control of the process of lactic acid fermentation and the removal of lactic acid bacteria from the wine after lactic acid fermentation. Lactic acid bacteria multiply in the process of lactic acid fermentation and usually completely alter the substrate of malic acid into a product of lactic acid. When they run out of the primary substrate, malic acid, they begin to metabolize other substances into the wine, which can have a significant negative effect on the taste of the wine. It is an object and object of the present invention to enable the control of lactic acid fermentation by isolating lactic acid bacteria from the wine at the appropriate stage of the lactic fermentation process or after completion of lactic acid fermentation. By eliminating bacteria, fermentation processes stop. The elimination of lactic acid bacteria is achieved by irreversible adsorption of magnetic particles onto their surfaces, which enables their removal from the must by using an external magnetic field. |
| Drawings: |
 |
| Category: |
Biological Sciences |
| Technology application codes: |
Biological sciences, Measurements and standards, Agrofood industry |
| Market application codes: |
Genetic engineering / molecular biology, Consumer related |
| www: |
https://worldwide.espacenet.com/patent/search/family/057359463/publication/SI24998A?q=SI24998 |
| Patent offices: |
UIL RS |


